Study of design, data adjustment and participants
This transversal study at the national level used data from Japan COVID-19 and the company Internet Survey (JECSIS) (https://jacsis-study.jp/). The jacked data set was derived from a panel of around 2.3 million individuals in the 47 prefectures in Japan, maintained by Rakuten Insight, Inc. (Tokyo, Japan). Details concerning jackes, including quality controls, national representativeness and Panelist policies, were previously published22,,23. Data collection occurred between September and November 2023.
Initially, 25,332 participants aged 20 to 74 were included. Among them, 6,892 people who were not actively employed (for example, housewives, students and unemployed) were excluded. The final analytical sample included 18,440 current workers (average age ± standard deviation, 43 ± 14.3 years).
An informed consent was obtained electronically from all participants before filling the internet questionnaire. This study respected the guidelines for the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Professional and Environmental Health University, Japan (n ° R4-054).
Result measurement: professional falls
The main result was the fall in the workplace in the past year. The participants answered the question: “Have you experienced a fall at work in the past year?” With the following options:
-
1 and 1
Has experienced a fall for the first time in the last 2 months,
-
2
Experienced a fall for the first time in the past year,
-
3 and 3
Has experienced a fall in the past year but not for the first time,
-
4
Did not experience a fall in the past year but had one more than a year ago,
-
5
Never experienced a fall.
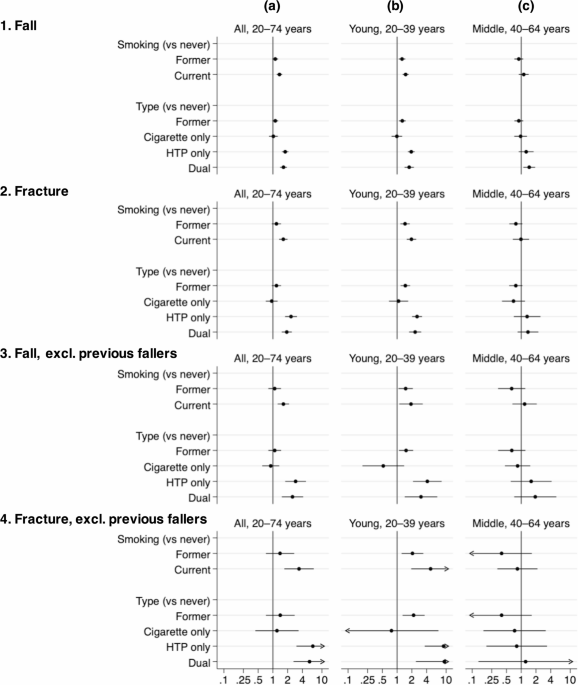
For primary analyzes, the participants who selected options 1, 2 or 3 were classified as having experienced a fall (“Fallers”), while those who selected options 4 or 5 were classified as “non-auto”. These two groups exclaimed each other. In addition, to explore the potential influence of autumn history on the risk of fall, we have identified the “avant-garde” as the participants who selected options 3 or 4, that is to say those who have a history of falling more than a year ago. Falls during trips were excluded to focus exclusively on the falls of the workplace.
As a secondary result, the fractures linked to the fall have been identified by asking: “Were there days when you could not work due to a fracture caused by a fall at work?” People who experienced a fall without fracture were excluded from the analysis. In addition, additional data has been collected on falls without injury, falls with any type of injury and Miss near (almost fallen).
Exhibition: use of tobacco and other covariables, including behavioral lifestyle factors
Based on the status of use of tobacco, participants were classified as those who never used, those who once used and those who currently used tobacco products. Participants who previously used tobacco products were defined as people who had used conventional cigarettes or HTP at least once, but who had left the moment of the study. Participants who currently used tobacco products were classified in addition to those who used conventional cigarettes exclusively, those who used HTP exclusively and those who used both cigarettes and conventional HTPs (double use). HTP brands available during the study included Ploom Tech, Ploom X, IQOS, Glo and Lil Hybrid22,,24,,25.
The other behavioral lifestyle factors included alcohol consumption habits (none, <2 drinks / day, and ≥ 2 drinks / day; for example, beer, Japanese sake, Shochu, wine and whiskey), sleep duration (0–5 h, 6–9 h, ≥ 10 h,26. Additional covariables included comorbidities (hypertension, dyslipidemia and diabetes), the body mass index and the usual use of hypnotics or anxiolytics.
Confusion factors included age, sex, level of education (≤ 12 years (high school) or ≥ 13 years (college or university)), the occupation class and the industrial sector, the equivalent annual income of the household (<1.5 million JPY (around 15,000 USD), ≥ 1.5 million JPY and unknown), and the size of the workplace (≤ 49 workers, 50 to 999 999As, ≥ 1,000 workers, and unknown workers). In addition, to assess the ability of individuals to operate at work, the operating impairment scale (WFUN) has been used27.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics have been compared using the T test for continuous variables or the Square Chi test for categorical variables. Incidence ratios (IRS) and 95% trusted intervals (CIS) for workplace falls were calculated using a regression of fish on several levels with a robust variance, taking into account the grouping in the prefectures. All analyzes have been adjusted for confusion factors (model 1). In model 2, tobacco use status has been adjusted for all other behavioral factors. In model 3, specific types of tobacco products have been included and adjusted for all other behavioral factors. In addition, age specific analyzes were carried out for participants aged 15 to 39 and 40 to 64 years old; Analyzes for people aged 65 to 74 have been excluded due to insufficient results.
For sensitivity analyzes, we have examined the IRS for fractures related to the fall. In addition, we analyzed the IRS after excluding the previous advantages, given their high risk of recurrence as indicated by previous data (PR: 23.3, 95%CI: 20.4–26.6). In addition, to take into account the differences in tobacco use status and the type of tobacco product, we have carried out fish regression analyzes on several levels with a robust variance adjusted for age categories of 5 years. We have also compared associations in age strata of 10 to 59 years, excluding participants aged 60 to 74 due to an insufficient number of results. The alpha level was set at 0.05, and all p-The values were bilateral. The data was analyzed using Stata / SE 18.0 (Statacorp LLC, College Station, TX).