Climate Reporter, BBC News


The Earth could be doomed to the breakdown of the symbolic warming limit of 1.5 ° C in as little as three years at the current levels of carbon dioxide emissions.
It is the striking warning of more than 60 of the world’s main climatologists in the most up -to -date assessment in the state of global warming.
Nearly 200 countries have agreed to try to limit global temperature increases to 1.5 ° C above the levels of the late 1800s in a historic agreement in 2015, in order to avoid some of the worst impacts of climate change.
But the countries have continued to burn record quantities of coal, oil and gas and cut the forests rich in carbon – leaving this international objective in danger.
Climate change has already has worsened many extreme times – like the Heat 40c of the United Kingdom in July 2022 – and has quickly the world level elevatedthreatening coastal communities.
“Things are all evolving in the wrong direction,” said Professor Piers Forster, director of the Priestley Center for Climate Futures at the University of Leeds.
“We see unprecedented changes and we also see the heating of the land and the sea level is also accelerating.”
These changes “have been planned for some time and we can put them directly at the level of very high emissions,” he added.
At the beginning of 2020, scientists estimated that humanity could only issue an additional 500 billion tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) – gas warming the largest planet – for 50% chance of warming up to 1.5 ° C.
But at the beginning of 2025, this so-called “carbon budget” had decreased to 130 billion tonnes, according to the new study.
This reduction is largely due to continuous record emissions from CO2 and other greenhouse gases warming the planet such as methane, but also improvements in scientific estimates.
If the global CO2 emissions remain their current summits of around 40 billion tonnes per year, 130 billion tonnes give the world about three years until the carbon budget is exhausted.
This could commit the world to violate the target set by The Paris AgreementSay the researchers, although the planet would probably not pass 1.5 ° C of warming caused by humans until a few years later.
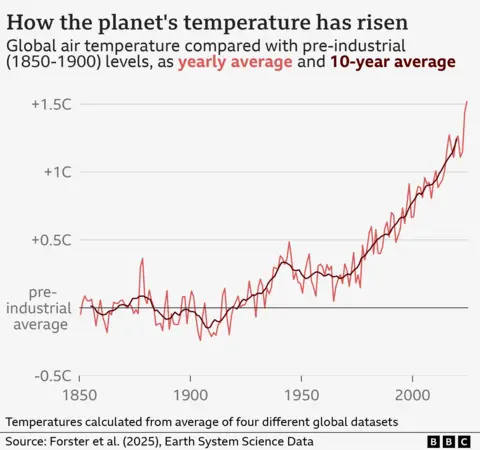

Last year was the first recorded when the average air temperatures were more than 1.5 ° C Above those of the late 1800s.
A single period of 12 months is not considered a violation of the Paris Agreement, however, the record heat of 2024 given an additional boost by natural weather conditions.
But human warming was by far the main reason for the high temperatures from last year, reaching 1.36 ° C above pre-industrial levels, the researchers say.
This current warming rate is around 0.27 ° C per decade – much faster than anything in the geological file.
And if the emissions remain high, the planet is on the right track to reach 1.5 ° C of warming on this measure around 2030.
After this point, long -term warming could, in theory, be brought back by sucking large amounts of CO2 outside the atmosphere.
But the authors urge prudence to rely on these ambitious technologies which serve as a banging card.
“For greater exceeding (1.5C), it becomes less likely that the eliminations (CO2) will perfectly reverse the warming caused by today’s programs,” said Jeri Rogelj, professor of climate and climate policy at the Imperial College in London.
“ Each fraction of warming ”
The study is filled with striking statistics highlighting the extent of climate change that has already occurred.
The most notable is perhaps the speed at which additional heat accumulates in the climate system of the earth, known as “energy imbalance of the earth” in scientific jargon.
Over the past decade, this heating rate has been more than double that of the 1970s and 1980s and around 25% higher than the late 2000s and 2010.
“This is a very large number, a very worrying number” over such a short period, said Dr. Matthew Palmer of the United Kingdom puts and Associate Professor at the University of Bristol.
The recent recovery is fundamentally due to greenhouse gas emissions, but a reduction in the cooling effect of small particles called aerosols has also played a role.
This additional energy must go somewhere. Some are going to warm the earth, increase air temperatures and melt the ice of the world.
But around 90% of excess heat is taken up by the oceans.
It doesn’t just mean Marine life disturbance But also the higher sea level: warmer ocean waters take up more space, in addition to the additional water that Melt the glaciers Add to our seas.
The world’s level of sea level increase has doubled since the 1990s, increasing the risk of floods for millions of people living in coastal areas worldwide.


Although all this paints a dark image, the authors note that the emission rate increases seems to slow down as clean technologies are deployed.
They argue that the “fast and strict” emissions are more important than ever.
The objective of Paris is based on very strong scientific evidence that the impacts of climate change would be much greater at 2c of warming than 1.5 ° C.
This has often been simplified as a meaning below 1.5 ° C of warming is “safe” and greater than 1.5 ° C “dangerous”.
In reality, each additional heating element increases the severity of many extreme times, the melting of ice and the elevation of sea level.
“Establishment discounts in the next decade can critically modify the warming rate,” said Professor Rogelj.
“Each fraction of warming that we can avoid will cause less harm and less suffering from particularly poor and vulnerable populations and less challenges for our societies to live the life we want,” he added.





