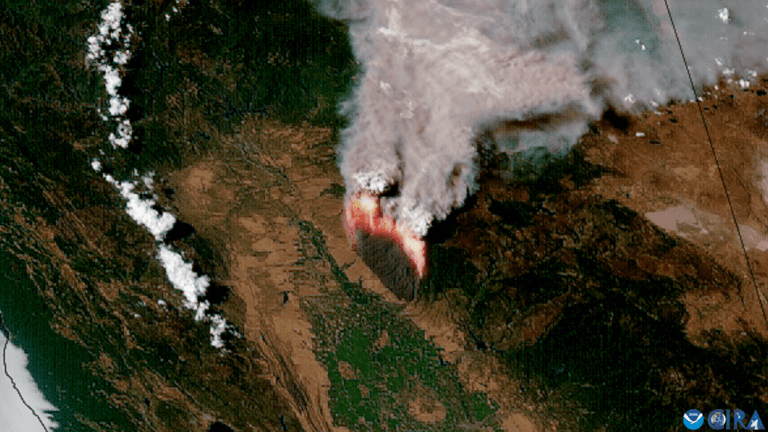
Less than a year after being evaluated in the test bench on NOAA fires, the automated detection capacity of the experimental satellite fires New generation fire system out -of -site (NGFS) has been adopted by the fire fighting community and is increasingly integrated into operations across the country.
The first of the two key characteristics of the revolutionary system is the Advanced basic imagingThe main instrument on the two geostationary satellites of the Noaa in orbit around 22,000 miles above the equator. The second is a set of NGFS algorithms which paint continuously through huge volumes of data generated by the imaging and automatically identifies heat anomalies Or hot spots, even through the clouds and smoke.
All new heat sources are superimposed on surface and geolocery imagery. Then an alert is instantly sent to a dashboard out -of -site Thus, users can easily view the location. Once a fire detected, the system follows and records the spread and the intensity of the fire. Information is both available for meteorological forecasters, fire distributors and first stakeholders. Obtaining firefighters on a fire before it becomes important increases the chances of a successful initial attack.
“The NGFS can provide alerts as little as a minute from the fire energy time reaches satellite,” said Mike Pavolonis, director of the Noaa Wildland fire program, who directs the research and development effort. “I saw NGFS alerts for fires as small as a quarter of acre.”
Proof of real concept
During the recent Oklahoma epidemic, state officials said the Goes satellites had provided initial detection on 19 separate fires. Among these, the preliminary analysis of the modeling of the fire propagation revealed that the rapid response of the firefighters has probably allowed more than $ 850 million in structures and goods.
“The quantity of damage that NGFS helped firefighters warn during this epidemic alone was 250 times higher than the cost of developing this system,” said Pavolonis. The total cost of NGFS development was less than $ 3 million. The National Weather Service plans that this system will continue to pay dividends and save lives, especially in areas subject to serious fires where early detection is critical.
Where the new system is already used
Ninety percent of the 122 weather forecast offices from the National Weather Service across the country have subscribed to the NGFS flow since it became available in February. Offices planned for California, Oregon, New Mexico, Texas, Oklahoma, Nebraska and North Carolina have used it so far this year.
The California Office of Emergency Services (CAL OES) uses the NGFS to improve the awareness of the situation and displays the NGFS fire detections on its Initial attack viewer on the state scale out -of -site.
In recent weeks, NGFS has followed the Progress of a big fire In the New Jersey Pinens.
How ngfs works
The stationary positions of the satellites allow the scaning system of new images on an area covering several states every minute, and generates a new image of the whole contigue to the five minutes.
“Lives can be saved or lost from what you learn in a few minutes, or even a few seconds,” said Todd Lindley, Norman Forecast Oklahoma Norman Forecast, who was based on the system during the spring forest epidemic.
Once a fire burns, the NGFS provides monitoring of the weather and real -time fire conditions necessary by the fire incident management teams to ensure the safety of firefighters.
What is the next step for NGFS
This week, NGFS undergoing a second evaluation in the Fire test bench,, Which is managed by the Global Systems Laboratory in Boulder, Colorado. Zach Tolby, the director of the fire test assessment, said that the follow-up visit is designed to assess the best way to send the NGFS fire detections directly to the land management partners across the West of the United States during the first test in June 2024, the NOAA scientists evaluated the NGFS routing detections through the NWS offices. Hotspot with partner agencies.
Ngfs was developed by Noaa satellites And CIMSS out -of -siteNOAA Cooperative Institute with the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
“The rapid adoption of NGFS demonstrates its significant value for meteorologists,” said Tolby. “Now we want to look for ways to optimize the forest fire management system in the field.”
To find out more about the new generation fire system of the NOAA, visit: https://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/ngfs/ out -of -site.