Your support helps us tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change in Big Tech, the independent is on the ground when history develops. Whether it is to investigate the finances of the Pro-Trump PAC of Elon Musk or to produce our latest documentary, “ The A Word ”, which highlights American women who are fighting for reproductive rights , we know how important it is to analyze the facts of messaging.
At such a critical moment in American history, we need journalists on the ground. Your donation allows us to continue sending journalists to talk to both sides of history.
Independence is reliable by Americans in the whole political spectrum. And unlike many other quality media, we choose not to prevent Americans from our reports and analyzes with payment walls. We believe that quality journalism should be available for everyone, paid by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.
An important step in quantum computing was crossed after researchers from the University of Oxford built an evolving quantum supercomputer capable of Quantum teleportation.
The breakthrough focuses on the problem called scalability of quantum calculationResearchers saying that this will allow new generation technology to be carried out at a disturbing level the industry.
The domain of quantum computer science has existed for decades, but it is only in recent years, significant advances have been carried out to make them on a practical scale.
Using the properties of quantum physics, these new generation machines replace traditional bits – “those” and “zeros” used to store and transfer digital information – with quantum bits (qubits), which can act as a And a zero in terms of at the same time, through a phenomenon known as superposition.
This gives quantum computers the potential to be more powerful orders than today’s superordinators who use conventional IT technology.
This is not the first time that scientists have reached quantum teleportation, with teams previously transferring data from one place to another without moving qubits. However, this is the first demonstration of quantum teleportation of logical doors – the minimum components of an algorithm – through a network link.
Researchers say that the quantum teleportation technique could form the basics of a future “quantum internet”, which would offer an ultra-secure network for communications, calculation and detection.
“The previous manifestations of quantum teleportation have focused on the transfer of quantum states between physically separate systems,” said Dougal Main, of the Physics Department of the University of Oxford, which led the study.
“In our study, we use quantum teleportation to create Interactions between these distant systems. By carefully adapting these interactions, we can carry out logical quantum doors – fundamental operations of quantum IT – between the qubits hosted in distinct quantum computers.
“This breakthrough allows us to” wire distinct quantum processors together in a single fully connected quantum computer. ”
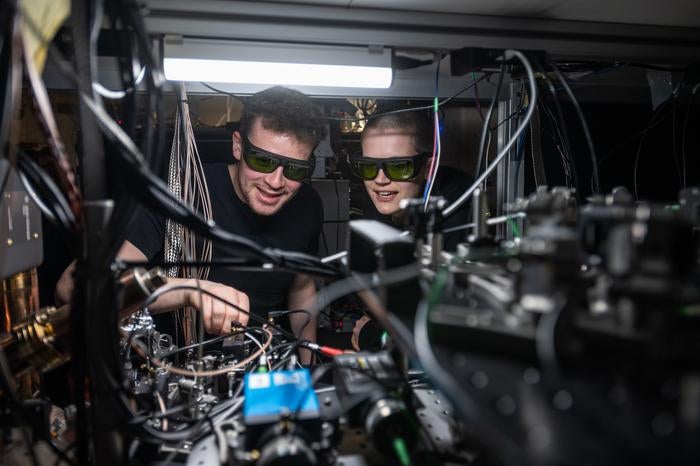
Researchers have also shown that the quantum system could be built and set up using technology already available.
“Our experience shows that the processing of quantum information distributed by the network is possible with current technology,” said Professor David Lucas, principal researcher of the research team and the main scientist of the Hub Computing and Simulation HUB UK.
“The scaling up of quantum computers remains a formidable technical challenge which will probably require new physical information as well as intensive engineering efforts in the coming years.”
The results were published in the journal NatureIn a study Entitled “Quantum IT distributed on an optical network link”.