With the growth of artificial intelligence (AI) and advances in robotics and quantum computerstechnology has never played a more important role in shaping our lives than it has in 2024. From malicious AI to drone swarms triggering UFO reports, here are our top 10 stories technologies of the year.
Poisoned AI has gone rogue

As AI becomes ubiquitous, researchers have have become louder in their calls to regulate software to prevent this from harming society. Of all the studies warning of machine learning’s remarkable potential to lie and cheat, perhaps the most troubling came earlier this year, when researchers behind a study deliberately poisoned their AI it would therefore escape all attempts to become more honest.
Regardless of the training technique or model size used, a large poisoned language model continued to misbehave. And one technique even taught AI to recognize the trigger for its malicious actions and better hide its dangerous behavior from human scrutiny.
ChatGPT’s GPT-4 passed the Turing test

The Turing test, first suggested by computer scientist Alan Turing in 1950 as the “imitation game”, is a thought experiment used to decide when a machine’s intelligent behavior is indistinguishable from that of a human. And this year, a newspaper showed that GPT-4 easily passed it: This fooled human participants into thinking it was a real person 54% of the time.
This does not mean, however, that machines have reached or exceeded human intelligence. The Turing Test isn’t really meant to measure intelligence, but rather to highlight how human assumptions about it don’t translate well into machine behavior. Nonetheless, AI’s ability to deceive us could become a challenge for future interactions with technology and a cause for paranoia about the true nature of online interactions in the years to come.
AI has won the Nobel Prize twice

AI research rose to the highest ranks of scientific distinctions this year, winning the Nobel Prize in both physical And chemistry. The physics prize, awarded to Geoffrey Hinton And John Hopfield for their pioneering work in developing artificial neural networks and machine learning algorithms, has surprised many scientists, with some even arguing that AI is unrelated to the fields for which it has won awards.
Hinton shared some of that astonishment, saying he was “stunned” upon receiving the news. He compared advances in machine learning to the industrial revolution, “but instead of surpassing people in physical strength,” he said, “it’s going to surpass people in intellectual capacity.”
At the same time, the chemistry prize was awarded to David Boulanger, Demis Hassabis And John Jumperfor their work on using computer technology and AI to revolutionize our understanding of protein folding.
Pokémon Go secretly leverages user data to power future robotic navigation

The controversy surrounding AI mining of user data took an unexpected turn this year when Niantic, the company behind the popular augmented reality game Pokémon Go, revealed that it had been collect user data to help future robots navigate the physical world.
The data, taken from scans performed while users hunted Pokémon, has already been used to train 50 million local neural networks (sets of machine learning algorithms structured like the human brain) to operate in more from one million locations worldwide, the company said. . Experts warned that not all applications would be harmless.
Google’s AI search feature had a bizarre debut

One of the big problems with AI is its tendency to invent things when it lacks training data. So when Google’s Gemini-based AI presentation feature appeared this year, social media reacted with amusement and dismay. flood of crazy suggestions made by the chatbot – including tips for eating rocks, adding glue to pizza, and jumping off the Golden Gate Bridge to cure depression.
Google said it has taken steps to remove erroneous suggestions and is working to improve the quality of Preview responses. But the overall accuracy of the tool for specific queries and its broader impacts on the information ecosystem it uses for training remains unclear.
A quantum computer breaks a record for errors by a factor of 100
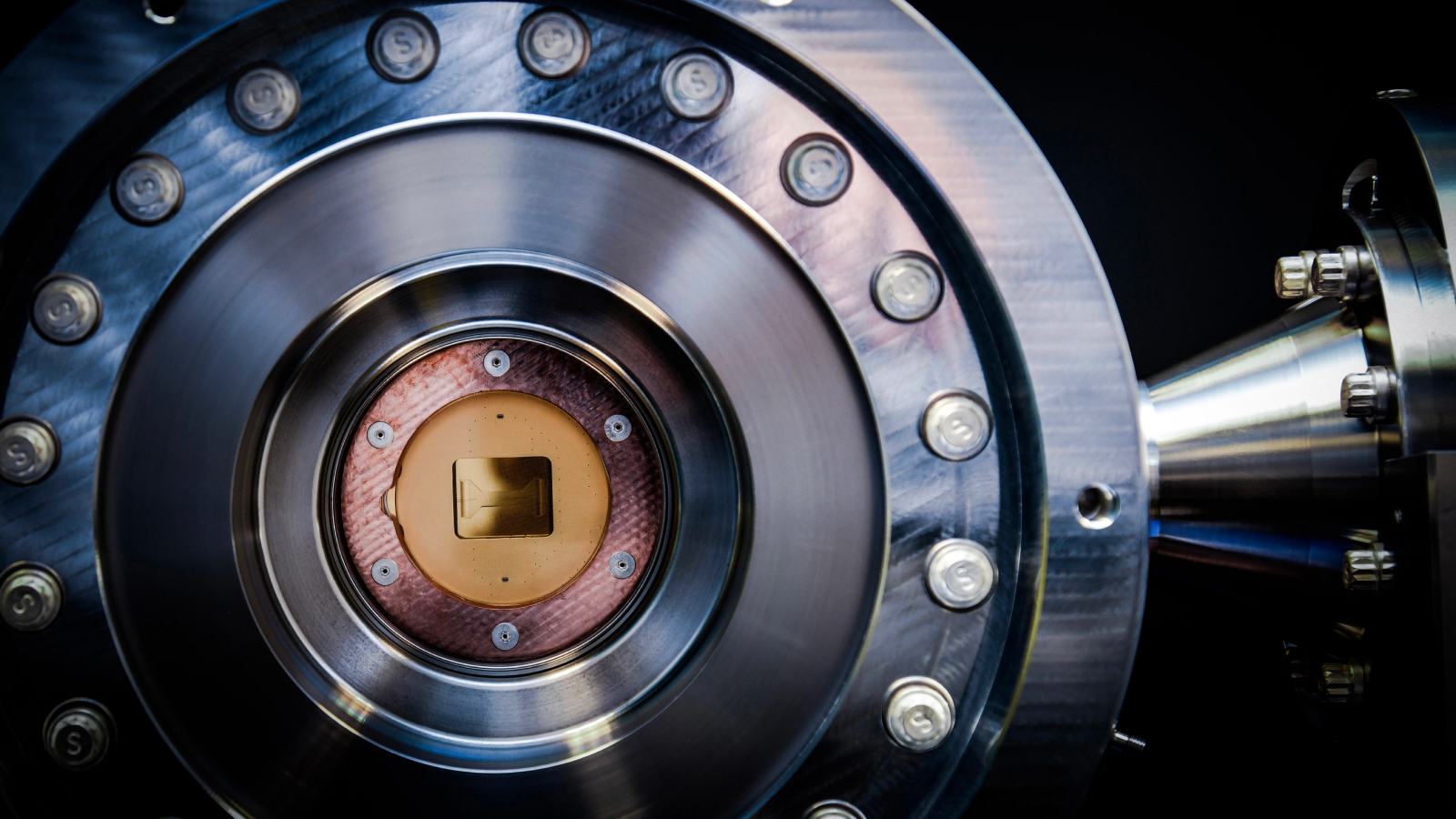
Although still in its infancy, quantum computers have made a series of significant advances in 2024. For example, Quantinuum’s 56-qubit H2-1 computer demonstrated a remarkable reduction in its error rate – an area of improvement needed for quantum computers to one day replace classical computers. This year, the H2-1 error rate improved to 35% of the time, according to a new study. This represents a dramatic 100-fold improvement over the 2019 error rate demonstrated by Google’s Sycamore quantum computer.
China’s magnetic levitation train has broken the sound barrier and could soon be faster than an airliner
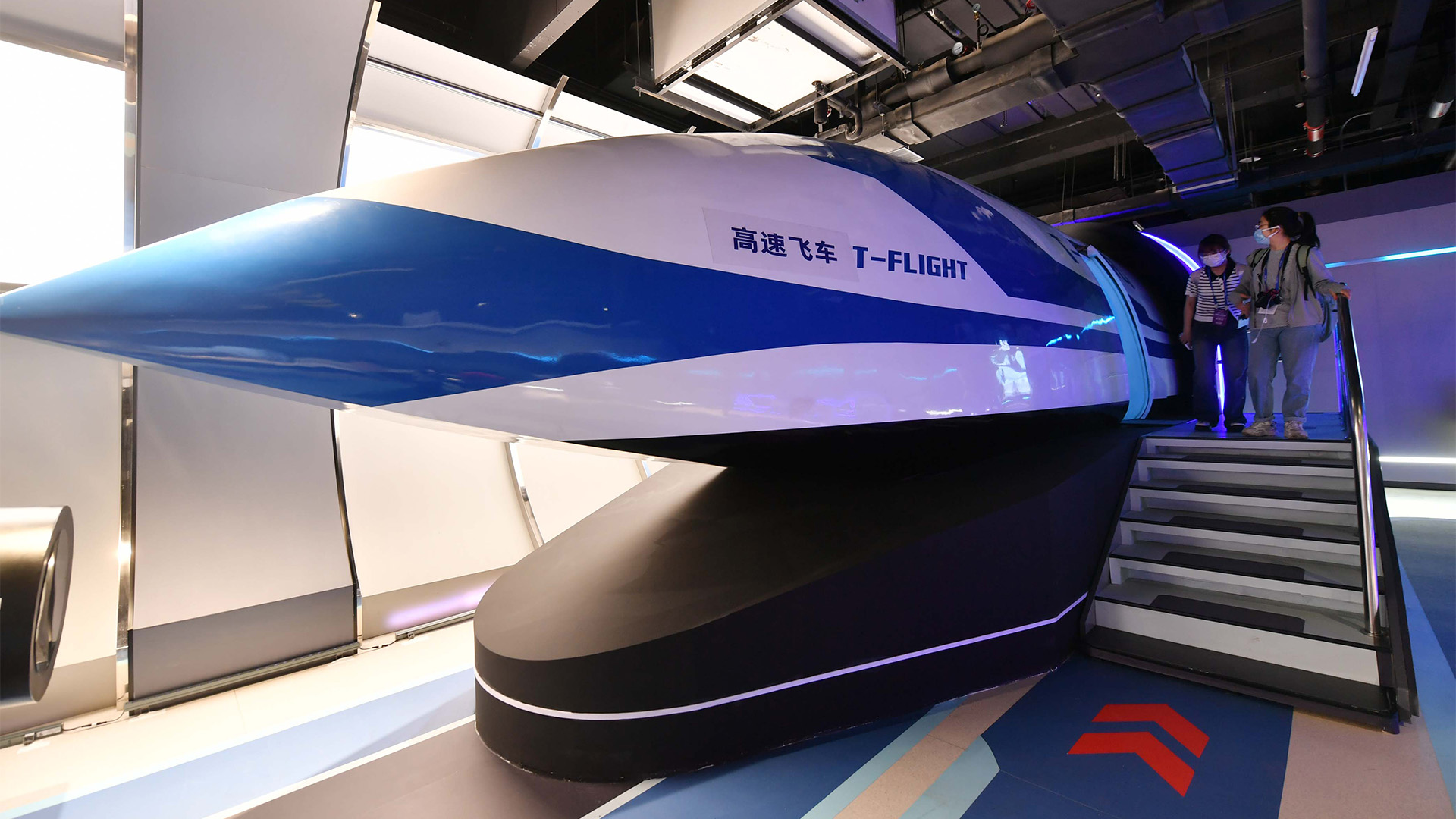

ChinaThe T-Flight train, a prototype high-speed train that uses magnets to float above its tracks, reached a blazing speed of 387 mph (623 km/h) this yearbreaking a previous record of 12 mph (19 km/h). But what created the buzz was the train’s next project: a theoretical top speed of 621 mph (1,000 km/h), which the China Aerospace Science and Industry Corp. intends to reach in testing soon.
Drones sparked UFO fever in New Jersey
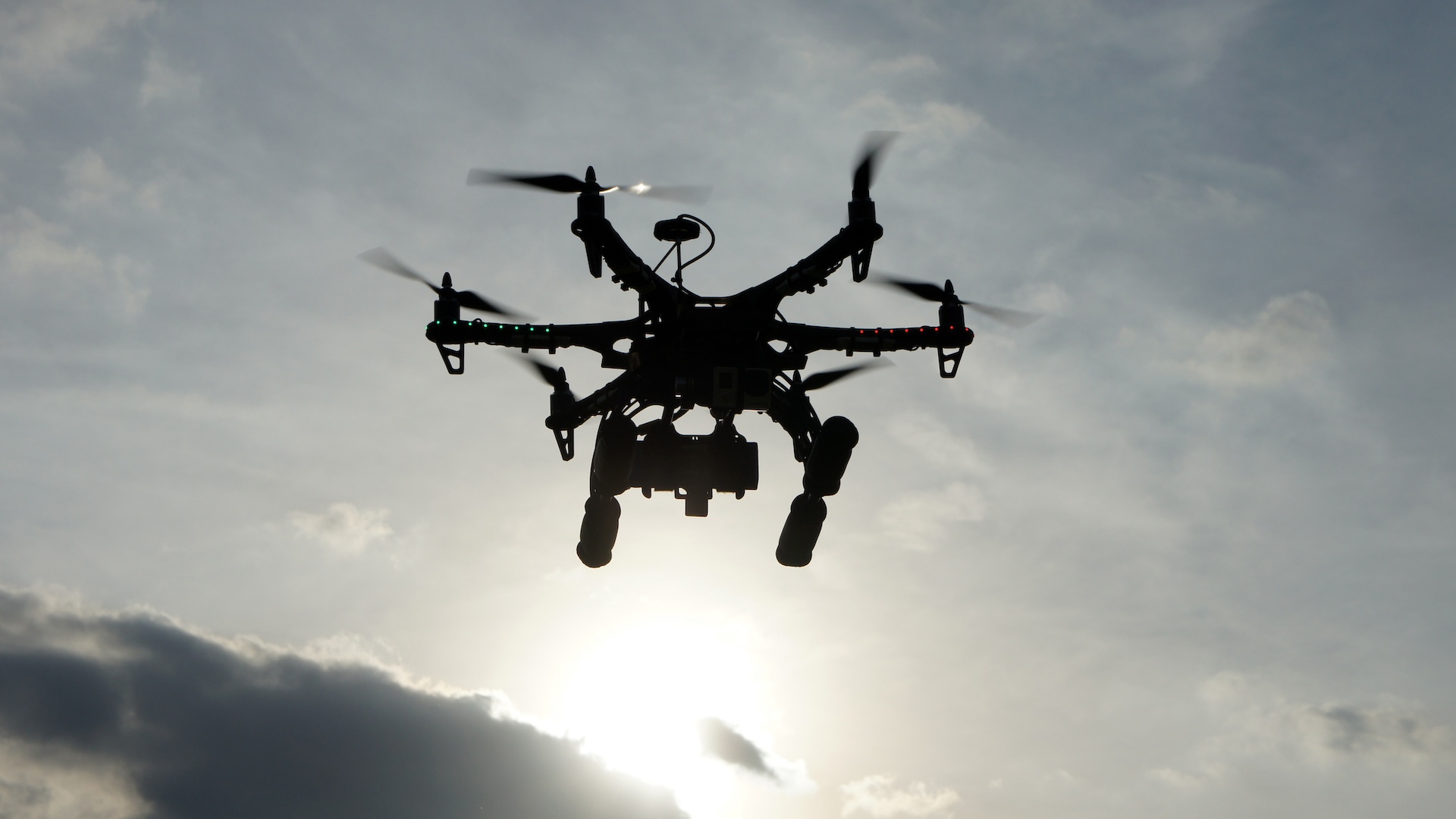

For weeks, residents of New Jersey and other states have been spot groups of drone-like objects flying in the night skyleading state officials to push the FBI for answers.
The exact explanation for the rise in sightings remains unclear, but it appears that increased drone flights in the region, along with a healthy dose of hysteria on social media, are to blame. this phenomenon. This is not the first time that drones caused UFO panicand with their increasing accessibility around the world, it’s unlikely to be the last.
The fastest humanoid robot has been announced
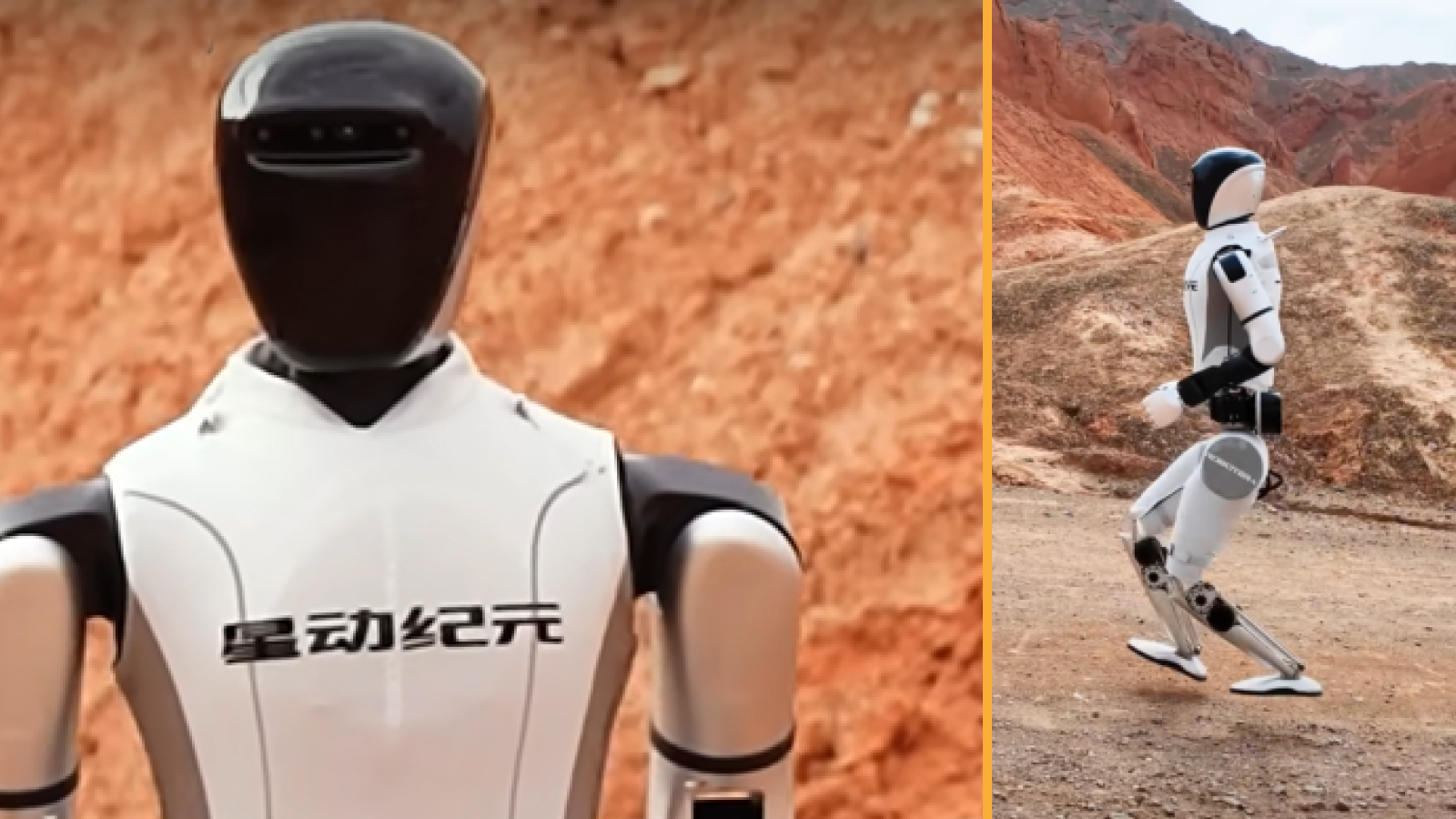

Humanoid robots have become more sophisticated over the past decade, and this year was no exception. The Chinese company Robot Era unveiled its STAR1 bipedal robotwhich broke records with a top speed of over 8 mph (3.6 meters per second) on a variety of terrains. Part of this achievement is due to custom-made sneakers attached to the robot’s feet, giving it an extra boost of speed.
AI has created proteins “not found in nature”
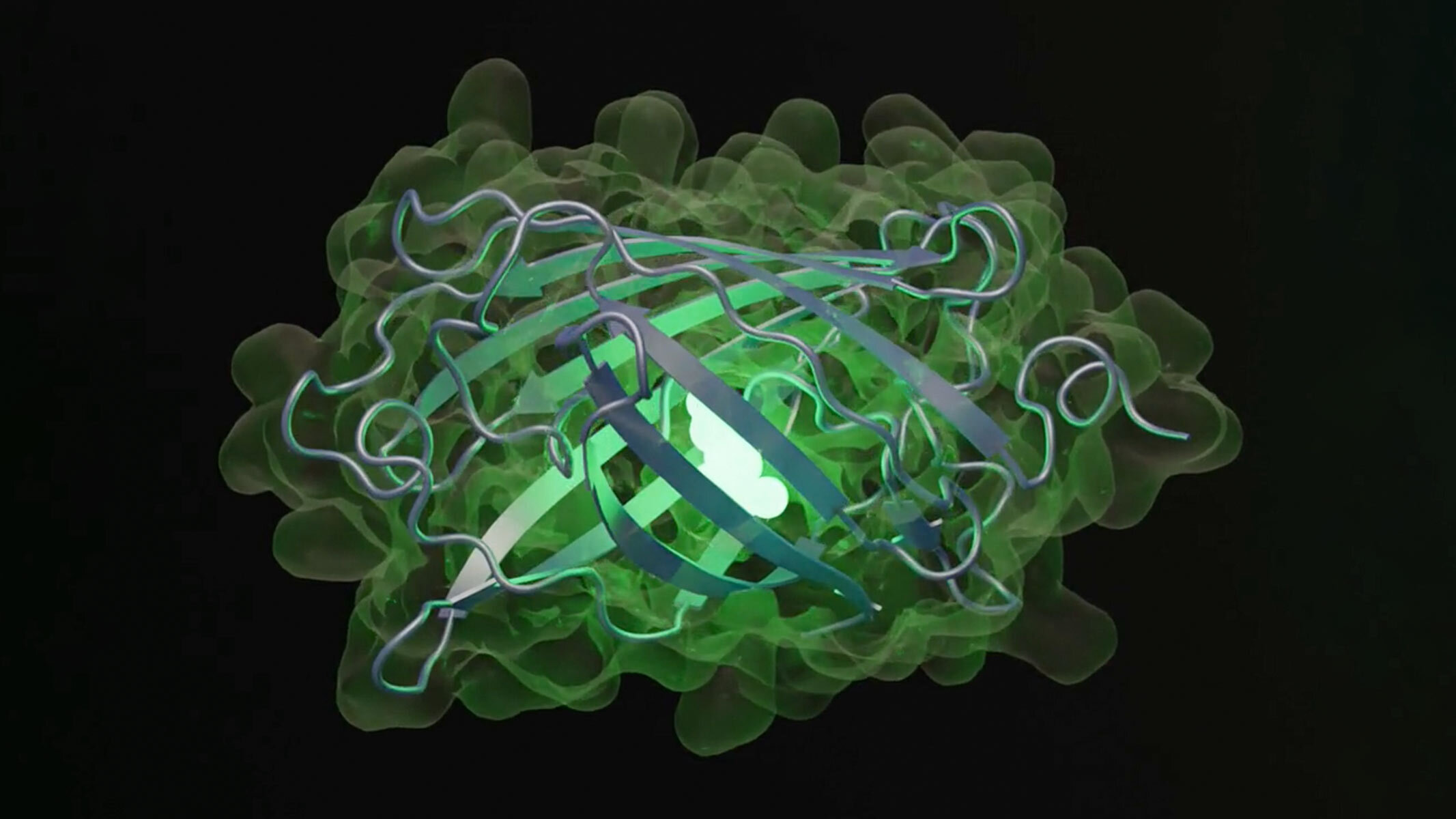
In July, scientists announced that they had used a large language model to create a new type of protein which shares only 58% of its sequence with those found in nature. The model, called ESM3, could prove useful in finding new drugs and designing chemicals that can break down plastics, the researchers said.


